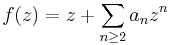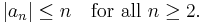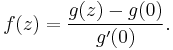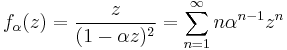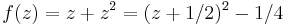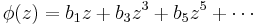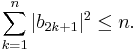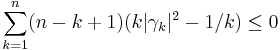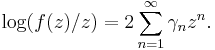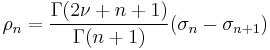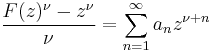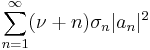de Branges's theorem
In complex analysis, de Branges's theorem, or the Bieberbach conjecture, is a theorem that gives a necessary condition on a holomorphic function in order for it to map the open unit disk of the complex plane injectively to the complex plane. It was posed by Ludwig Bieberbach (1916) and finally proven by Louis de Branges (1985).
The statement concerns the Taylor coefficients an of such a function, normalized as is always possible so that a0 = 0 and a1 = 1. That is, we consider a holomorphic function of the form
which is defined and injective on the open unit disk (such functions are also called univalent or schlicht functions). The theorem then states that
Contents |
Schlicht functions
The normalizations
- a0 = 0 and a1 = 1
mean that
- f(0) = 0 and f '(0) = 1;
this can always be assured by a linear fractional transformation: starting with an arbitrary injective holomorphic function g defined on the open unit disk and setting
Such functions g are of interest because they appear in the Riemann mapping theorem.
A family of schlicht functions are the rotated Köbe functions
with α a complex number of absolute value 1. If f is a schlicht function and |an| = n for some n ≥ 2, then f is a rotated Köbe function.
The condition of de Branges' theorem is not sufficient to show the function is schlicht, as the function
shows: it is holomorphic on the unit disc and satisfies |an|≤n for all n, but it is not injective since f(−1/2 + z) = f(−1/2 − z).
History
Bieberbach (1916) proved |a2| ≤ 2, and stated the conjecture that |an| ≤ n. Loewner (1917) and Nevanlinna (1921) independently proved the conjecture for starlike functions. Then Charles Loewner (Löwner (1923)) proved |a3| ≤ 3, using the Löwner equation. His work was used by most later attempts, and is also applied in the theory of Schramm–Loewner evolution.
Littlewood (1925, theorem 20) proved that |an| ≤ en for all n, showing that the Bieberbach conjecture is true up to a factor of e = 2.718... Several authors later reduced the constant in the inequality below e.
If f(z) = z + ... is a schlicht function then φ(z) = f(z2)1/2 is an odd schlicht function. Paley and Littlewood (1932) showed that bk ≤ 14 for all k. They conjectured that 14 can be replaced by 1 as a natural generalization of the Bieberbach conjecture. The Littlewood–Paley conjecture easily implies the Bieberbach conjecture using the Cauchy inequality, but it was soon disproved by Fekete & Szegö (1933), who showed there is an odd schlicht function with b5 = 1/2 + exp(−2/3) = 1.013..., and that this is the maximum possible value of b5. (Milin later showed that 14 can be replaced by 1.14., and Hayman showed that the numbers bk have a limit less than 1 if φ is not a Koebe function, so Littlewood and Paley's conjecture is true for all but a finite number of coefficients of any function.) A weaker form of Littlewood and Paley's conjecture was found by Robertson (1936).
The Robertson conjecture states that if
is an odd schlicht function in the unit disk with b1=1 then for all positive integers n,
Robertson observed that his conjecture is still strong enough to imply the Bieberbach conjecture, and proved it for n = 3. This conjecture introduced the key idea of bounding various quadratic functions of the coefficients rather than the coefficients themselves, which is equivalent to bounding norms of elements in certain Hilbert spaces of schlicht functions.
There were several proofs of the Bieberbach conjecture for certain higher values of n, in particular Garabedian & Schiffer (1955) proved |a4| ≤ 4, Ozawa (1969) and Pederson (1968) proved |a6| ≤ 6, and Pederson & Schiffer (1972) proved |a5| ≤ 5.
Hayman (1955) proved that the limit of an/n exists, and has absolute value less than 1 unless f is a Koebe function. In particular this showed that for any f there can be at most a finite number of exceptions to the Bieberbach conjecture.
The Milin conjecture states that for each simple function on the unit disk, and for all positive integers n,
where the logarithmic coefficients γn of f are given by
Milin (1977) showed using the Lebedev–Milin inequality that the Milin conjecture (later proved by de Branges) implies the Robertson conjecture and therefore the Bieberbach conjecture.
Finally De Branges (1985) proved |an| ≤ n for all n.
De Branges's proof
The proof uses a type of Hilbert spaces of entire functions. The study of these spaces grew into a sub-field of complex analysis and the spaces come to be called de Branges spaces and the functions de Branges functions. De Branges proved the stronger Milin conjecture (Milin 1971) on logarithmic coefficients. This was already known to imply the Robertson conjecture (Robertson 1936) about odd univalent functions, which in turn was known to imply the Bieberbach conjecture about simple functions (Bieberbach 1916). His proof uses the Loewner equation, the Askey–Gasper inequality about Jacobi polynomials, and the Lebedev–Milin inequality on exponentiated power series.
De Branges reduced the conjecture to some inequalities for Jacobi polynomials, and verified the first few by hand. Walter Gautschi verified more of these inequalities by computer for de Branges (proving the Bieberbach conjecture for the first 30 or so coefficients) and then asked Richard Askey if he knew of any similar inequalities. Askey pointed out that Askey & Gasper (1976) had proved the necessary inequalities eight years before, which allowed de Branges to complete his proof. The first version was very long and had some minor mistakes which caused some skepticism about it, but these were corrected with the help of members of the Leningrad Department of Steklov Mathematical Institute when de Branges visited in 1984.
De Branges proved the following result, which for ν = 0 implies the Milin conjecture (and therefore the Bieberbach conjecture). Suppose that ν > −3/2 and σn are real numbers for positive integers n with limit 0 and such that
is non-negative, non-increasing, and has limit 0. Then for all Riemann mapping functions F(z) = z + ... univalent in the unit disk with
the maximinum value of
is achieved by the Koebe function z/(1 − z)2.
References
- Askey, Richard; Gasper, George (1976), "Positive Jacobi polynomial sums. II", American Journal of Mathematics (American Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 98, No. 3) 98 (3): 709–737, doi:10.2307/2373813, ISSN 0002-9327, JSTOR 2373813, MR0430358
- Baernstein, Albert; Drasin, David; Duren, Peter et al., eds. (1986), The Bieberbach conjecture, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, 21, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, pp. xvi+218, ISBN 978-0-8218-1521-2, MR875226
- Bieberbach, L. (1916), "Über die Koeffizienten derjenigen Potenzreihen, welche eine schlichte Abbildung des Einheitskreises vermitteln", Sitzungsber. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. Phys-Math. Kl.: 940–955
- Conway, John B. (1995), Functions of One Complex Variable II, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-94460-9
- de Branges, Louis (1985), "A proof of the Bieberbach conjecture", Acta Mathematica 154 (1): 137–152, doi:10.1007/BF02392821, MR772434
- de Branges, Louis (1987), "Underlying concepts in the proof of the Bieberbach conjecture", Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, Vol. 1, 2 (Berkeley, Calif., 1986), Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, pp. 25–42, MR934213
- Drasin, David; Duren, Peter; Marden, Albert, eds. (1986), Proceedings of the symposium on the occasion of the proof of the Bieberbach conjecture held at Purdue University, West Lafayette, Ind., March 11—14, 1985, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, 21, Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, pp. xvi+218}, ISBN 0-8218-1521-0, MR875226
- Fekete, M.; Szegö, G. (1933), "Eine Bemerkung Über Ungerade Schlichte Funktionen", J. London Math. Soc. s1-8 (2): 85–89, doi:10.1112/jlms/s1-8.2.85
- Goluzina, E.G. (2001), "Bieberbach conjecture", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=B/b016150
- Hayman, W. K. (1955), "The asymptotic behaviour of p-valent functions", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. Third Series 5 (3): 257–284, doi:10.1112/plms/s3-5.3.257, MR0071536
- Korevaar, Jacob (1986), "Ludwig Bieberbach's conjecture and its proof by Louis de Branges", The American Mathematical Monthly (The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 93, No. 7) 93 (7): 505–514, doi:10.2307/2323021, ISSN 0002-9890, JSTOR 2323021, MR856290
- Littlewood, J. E. (1925), "On Inequalities in the Theory of Functions", Proc. London Math. Soc. s2-23: 481–519, doi:10.1112/plms/s2-23.1.481
- Littlewood, J.E.; Paley, E. A. C. (1932), "A Proof That An Odd Schlicht Function Has Bounded Coefficients", J. London Math. Soc. s1-7 (3): 167–169, doi:10.1112/jlms/s1-7.3.167
- Loewner, C. (1917), "Untersuchungen über die Verzerrung bei konformen Abbildungen des Einheitskreises /z/ < 1, die durch Funktionen mit nicht verschwindender Ableitung geliefert werden", Ber. Verh. Sachs. Ges. Wiss. Leipzig 69: 89-106
- Loewner, C. (1923), "Untersuchungen über schlichte konforme Abbildungen des Einheitskreises. I", Math. Ann. 89: 103–121, doi:10.1007/BF01448091, JFM 49.0714.01
- Milin, I. M. (1977), Univalent functions and orthonormal systems, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, MR0369684 (Translation of the 1971 Russian edition)
- Nevanlinna, R. (1921), "Über die konforme Abbildung von Sterngebieten", Ofvers. Finska Vet. Soc. Forh. 53: 1-21
- Robertson, M. S. (1936), "A remark on the odd schlicht functions", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 42 (6): 366–370, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1936-06300-7, http://www.ams.org/bull/1936-42-06/S0002-9904-1936-06300-7/